LeetCodeCampsDay20二叉树part07
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科 中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。”
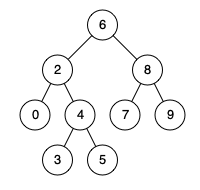
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 输出: 6 解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 输出: 2 解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
递归思路
本题是BST,可以利用它的特性;如果node大于q.val且大于p.val,则需要向左遍历,在左子树中找公共祖先节点;如果node小于q.val且小于p.val,需要向右遍历,在右子树中找公共祖先节点;否则,直接返回node, node一定为p和q的公共祖先节点
递归代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution : def foo (self, node, p, q ) -> TreeNode: if node == q or node == p or not node: return node if node.val > p.val and node.val > q.val: leftNode = self.foo(node.left, p, q) if leftNode: return leftNode if node.val < p.val and node.val < q.val: rightNode = self.foo(node.right, p, q) if rightNode: return rightNode return node def lowestCommonAncestor (self, root: 'TreeNode' , p: 'TreeNode' , q: 'TreeNode' ) -> 'TreeNode' : return self.foo(root, p, q)
迭代思路
因为BST已经排序好了,所以不需要借用栈就能自行搜索,迭代的代码反而更简单,如果同时将node与p&q的值对比,如果相等就返回node;否则就继续搜索
这与在BST中搜索target的代码几乎一样700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution : def findTarget (self, node: TreeNode, val: int ) -> TreeNode: if not node: return None if node.val > val: leftNode = self.findTarget(node.left, val) if leftNode: return leftNode elif node.val < val: rightNode = self.findTarget(node.right, val) if rightNode: return rightNode return node def searchBST (self, root: Optional [TreeNode], val: int ) -> Optional [TreeNode]: while root is not None : if root.val == val: return root elif root.val < val: root = root.right else : root = root.left return root
迭代代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 def lowestCommonAncestor (self, root: 'TreeNode' , p: 'TreeNode' , q: 'TreeNode' ) -> 'TreeNode' : if not root: return None node = root while node: if node.val > q.val and node.val > p.val: node = node.left elif node.val < q.val and node.val < p.val: node = node.right else : return node return None
701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/
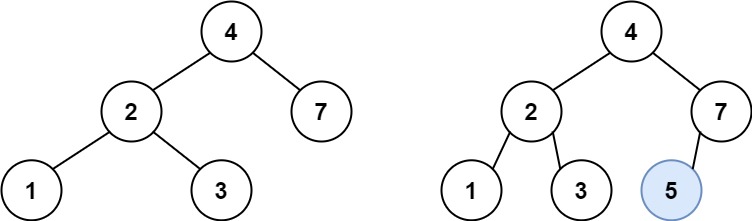
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意 ,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5] 解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:
示例 2:
1 2 输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25 输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
示例 3:
1 2 输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]
提示:
树中的节点数将在 [0, 104]的范围内。
-108 <= Node.val <= 108所有值 Node.val 是 独一无二 的。
-108 <= val <= 108保证 val 在原始BST中不存在。
递归思路
需要考虑递归是否需要带输出,如果带输出,输出需要是更新后的输入节点;如果不带输出,如何将更新后的节点表示出来
输入输出:输入节点与targetval, 输出插好的子树节点node
终止条件:如果遇到空节点,这个空节点就必然是targetVal应该在的地方(因为后面的单层逻辑必须保证这个条件)
单层逻辑:node.val与val判断,如果node.val大于val,则在node.left继续搜索,且node.left = foo(node.left, val);否则就在node.right搜索,注意这里的foo返回值是node.left或node.right已经将val插好后的新节点
递归代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def foo (self, node, val ): if not node: return TreeNode(val) if node.val < val: node.right = self.foo(node.right, val) if node.val > val: node.left = self.foo(node.left, val) return node def insertIntoBST (self, root: Optional [TreeNode], val: int ) -> Optional [TreeNode]: return self.foo(root, val)
迭代代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 def insertIntoBST (self, root: Optional [TreeNode], val: int ) -> Optional [TreeNode]: if not root: return TreeNode(val) partent = root cur = root while cur: partent = cur if cur.val > val: cur = cur.left elif cur.val < val: cur = cur.right if partent.val > val: partent.left = TreeNode(val) elif partent.val < val: partent.right = TreeNode(val) return root
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key ,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点;
如果找到了,删除它。
示例 1:
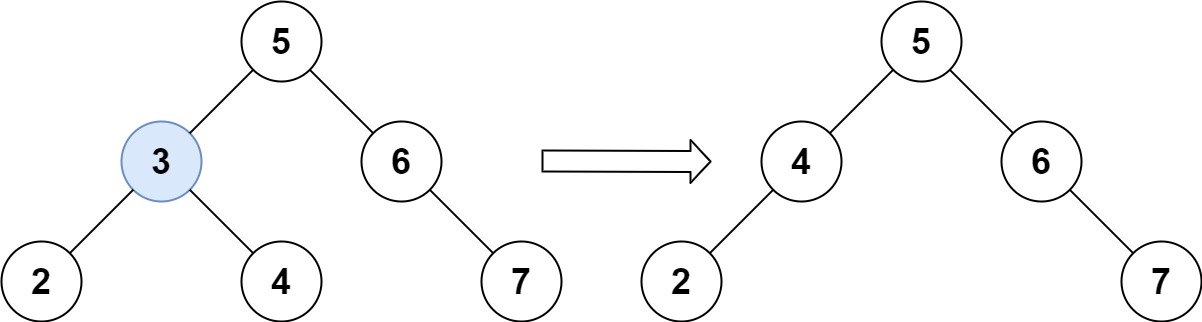
1 2 3 4 5 输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 输出:[5,4,6,2,null,null,7] 解释:给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。 一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。 另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 输出: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] 解释: 二叉树不包含值为 0 的节点
示例 3:
1 2 输入: root = [], key = 0 输出: []
提示:
节点数的范围 [0, 104].
-105 <= Node.val <= 105节点值唯一
root 是合法的二叉搜索树-105 <= key <= 105
进阶: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
递归思路
下面的方法节点位置发生了变化,当然还有种思路是直接在被删除节点的右子树里找到最小值,替换当前节点值即可,从而可以不改变位置
使用带返回值的递归方法,返回的内容是已经将节点删除后的节点
输入值node与key,输出是将key删除后的节点
终止条件:如果node为空则直接返回node;
单层逻辑:判断node.val与key的关系,直到找到node.val等于key,随后需要分四种情况
node的左、右子树为空,可以放心删除,直接返回None
node的左子树为空,右子树不为空;直接返回右子树
node的左子树不空,右子树为空,直接返回左子树
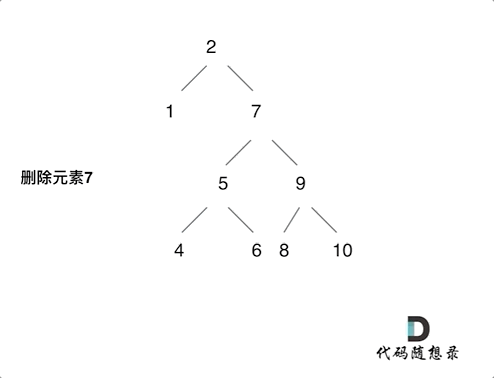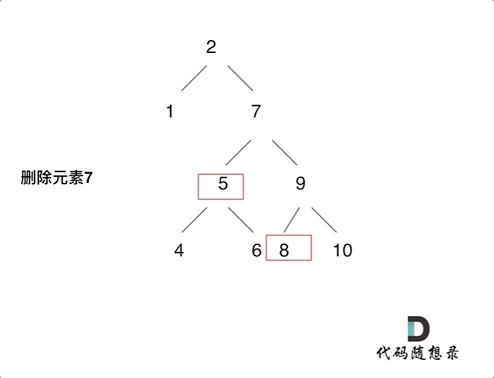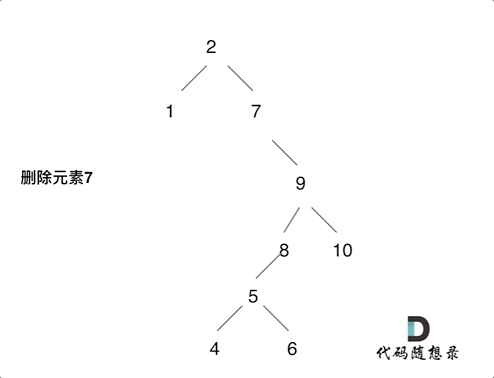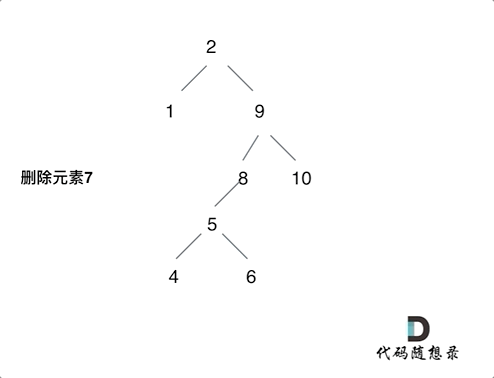
node的左、右子树都不空,当时需要特殊处理;将node左子树的root,变成node的右子树的最小的节点的左子树(参考下图),此时可以用个cur节点和while搭配,一直向左找即可
递归代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution : def __init__ (self ): self.parent = None def foo (self, node: TreeNode, key: int ) -> TreeNode: if not node: return node if node.val == key: if node.left is None and node.right is None : return None elif node.left is None and node.right: return node.right elif node.left and node.right is None : return node.left else : cur = node.right while cur.left: cur = cur.left cur.left = node.left node = node.right return node if node.val < key: node.right = self.foo(node.right, key) if node.val > key: node.left = self.foo(node.left, key) return node def deleteNode (self, root: Optional [TreeNode], key: int ) -> Optional [TreeNode]: return self.foo(root, key)
迭代代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 def deleteNode (self, root: Optional [TreeNode], key: int ) -> Optional [TreeNode]: if not root: return root parent = None node = root while node: if node.val == key: break parent = node if node.val > key: node = node.left elif node.val < key: node = node.right if parent is None : return self.deleteOneNode(node) if parent.left and parent.left.val == key: parent.left = self.deleteOneNode(parent.left) if parent.right and parent.right.val == key: parent.right = self.deleteOneNode(parent.right) return root
删除普通二叉搜索树的节点
在450基础上进行扩展
这里我在介绍一种通用的删除,普通二叉树的删除方式(没有使用搜索树的特性,遍历整棵树),用交换值的操作来删除目标节点。
代码中目标节点(要删除的节点)被操作了两次:
删除的逻辑时,在要被删除的node的右子树里,找到右子树最小的值,替换到node的值就好了,节点位置不用发生变化
第一次是和目标节点的右子树最左面节点交换。
第二次直接被NULL覆盖了。
递归代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 def bar (self, node, key ) -> TreeNode: if not node: return node if node.val == key: if node.right is None : return node.left cur = node.right while cur.left: cur = cur.left node.val, cur.val = cur.val, node.val node.left = self.bar(node.left, key) node.right = self.bar(node.right, key) return node